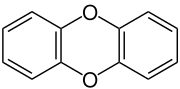
Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin
| |

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Oxanthrene[1] | |
| Other names
Dibenzodioxin,
Dibenzo-p-dioxin, Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 143227 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.432 |
| EC Number |
|
| 280302 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 184.194 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 122 °C (252 °F; 395 K) |
| Boiling point | 283.5 °C (542.3 °F; 556.6 K) |
| 0.901 g/L (25 °C) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H411 | |
| P264, P270, P273, P301+P312, P330, P391, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
polychlorinated dibenzodioxins ("dioxin"), dioxins and dioxin-like compounds |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, also dibenzodioxin or dibenzo-p-dioxin (dibenzo-para-dioxin), is a polycyclic heterocyclic organic compound in which two benzene rings are connected by a 1,4-dioxin ring. Its molecular formula is C12H8O2. The two oxygen atoms occupy opposite (para-) positions in the six-membered dioxin ring.
Dibenzodioxin is the carbon skeleton of the poisonous polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs), often called dioxins. The most harmful PCDD is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin (TCDD). Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds is a category of pollutants that includes PCDDs and other compounds that have similar structure, toxicity, and persistence. Dibenzodioxin is also the skeleton of the polybrominated dibenzodioxins.
Isomer
[edit]The general name dibenzodioxin usually refers to dibenzo-p-dioxin.
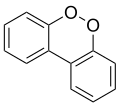
The isomeric compound dibenzo-o-dioxin (dibenzo-ortho-dioxin) or dibenzo-1,2-dioxin, like the unstable 1,2-dioxin, has two adjacent oxygen atoms (ortho-). No detailed information is available on this isomer, but it is expected to be highly unstable, with peroxide-like characteristics.
See also
[edit]- Thianthrene, the sulfur analog of dibenzodioxin
References
[edit]This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2021) |
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 216. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-00130. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
