Mixed anomaly
In theoretical physics, a mixed anomaly is an example of an anomaly: it is an effect of quantum mechanics — usually a one-loop diagram — that implies that the classically valid general covariance and gauge symmetry of a theory of general relativity combined with gauge fields and fermionic fields cannot be preserved simultaneously in the quantum theory.
The adjective "mixed" usually refers to a mixture of a gravitational anomaly and gauge anomaly, but may also refer to a mixture of two different gauge groups tensored together, like the SU(2) and the U(1) of the Standard Model.
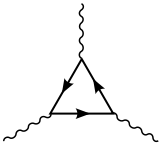
The anomaly usually appears as a Feynman diagram with a chiral fermion running in the loop (a polygon) with n−k external gravitons and k external gauge bosons attached to the loop where where is the spacetime dimension. Chiral fermions only occur in even spacetime dimensions. For example, the anomalies in the usual 4 spacetime dimensions arise from triangle Feynman diagrams.
General covariance and gauge symmetries are very important symmetries for the consistency of the whole theory, and therefore all gravitational, gauge, and mixed anomalies must cancel out.
References[edit]
- Cheng, T.P.; Li, L.F. (1984). Gauge Theory of Elementary Particle Physics. Oxford Science Publications.
See also[edit]